Zero Trust is a security model that assumes that every request, regardless of its origin, should be verified before granting access to resources. This model is based on the principle of “never trust, always verify” and is designed to protect against modern cybersecurity threats. Microsoft has adopted a Zero Trust strategy to secure corporate and customer data, and Microsoft 365 is built with many security and information protection capabilities to help organizations build Zero Trust into their environment.
Here are some key principles and elements of the Zero Trust model in Microsoft 365:
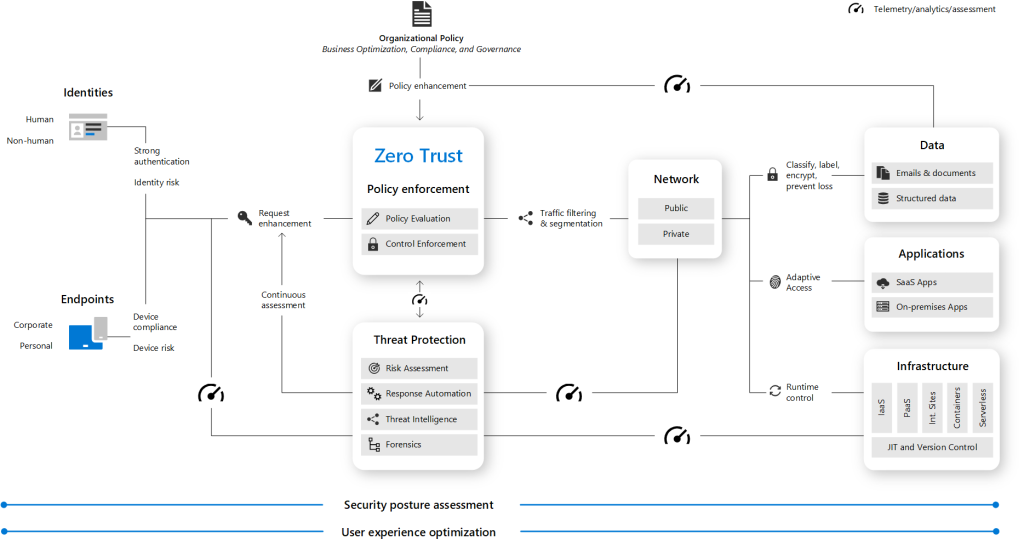
Guiding Principles of Zero Trust:
- Verify explicitly: Always authenticate and authorize based on all available data points, including user identity, device health, service or workload, data classification, and anomalies.
- Use least privileged access: Limit user access with just-in-time and just-enough-access (JIT/JEA), risk-based adaptive policies, and data protection to protect both data and productivity.
- Assume breach: Minimize blast radius for breaches and prevent lateral movement by segmenting access by network, user, devices, and application awareness.
- Always verify: Continuously validate the trustworthiness of the devices and sources of access, and prevent access from compromised networks and devices.
Foundational Elements of Zero Trust:
- Identity: Ensure strong user authentication and access policies, and use multi-factor authentication (MFA) and conditional access policies to protect against identity-based attacks.
- Devices: Verify device health and compliance with security policies, and use mobile device management (MDM) and endpoint detection and response (EDR) to protect against device-based attacks.
- Applications: Protect applications and data with access policies, data classification, and encryption, and use application protection and monitoring to protect against application-based attacks.
- Networks: Segment networks and use virtual private networks (VPNs) and software-defined perimeters (SDPs) to protect against network-based attacks.
- Data: Classify data and use data protection and encryption to protect against data-based attacks.
- Infrastructure: Use cloud security posture management (CSPM) and security information and event management (SIEM) to protect against infrastructure-based attacks.
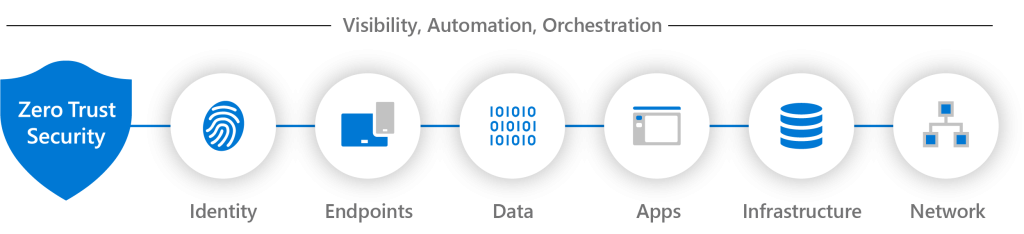
To implement Zero Trust in Microsoft 365, organizations can follow a deployment plan that includes steps such as deploying identity infrastructure, configuring identity and device compliance policies, managing endpoints with Microsoft 365 Defender, and deploying information protection for data privacy regulations. Microsoft also provides setup and advanced deployment guides for Zero Trust with Microsoft.
In summary, the Zero Trust model in Microsoft 365 is a comprehensive security framework that helps organizations protect against modern cybersecurity threats by verifying every request and enforcing the least privileged access. By adopting Zero Trust, organizations can simplify security with a strategy, processes, and automated tools that protect people, devices, applications, and data wherever they are located.

