In today’s digital-first world, the traditional security perimeter has all but disappeared. Employees work remotely, applications live in the cloud, and cyber threats are more sophisticated than ever. To meet this challenge, organizations are embracing the Zero Trust Model — a security framework built on the principle of “never trust, always verify.”
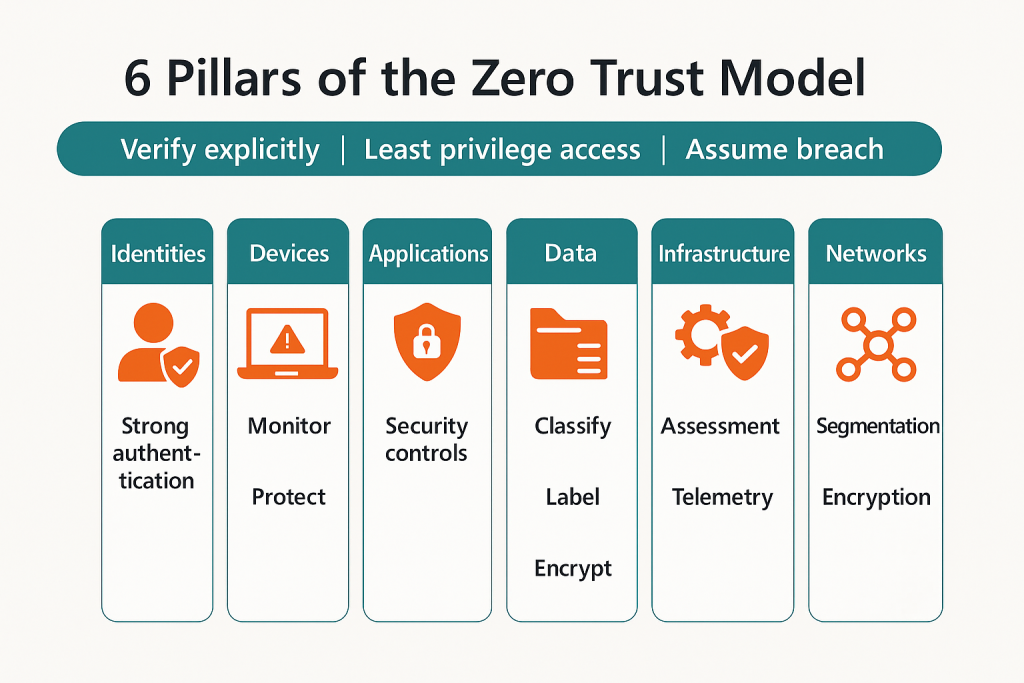
At the heart of Zero Trust are six foundational pillars that help protect identities, devices, applications, data, infrastructure, and networks. Together, they create a holistic, adaptive security posture that assumes breaches will happen and prepares defenses accordingly.
1. Identities: Strong Authentication
Every user must prove who they are — every time. Zero Trust enforces multi-factor authentication (MFA), conditional access policies, and behavioral analytics to verify identities explicitly before granting access.
🔑 Key takeaway: Identity is the new perimeter. Protect it relentlessly.
2. Devices: Monitor and Protect
With countless laptops, mobile phones, and IoT devices connecting to business systems, device health is critical. Zero Trust continuously monitors device compliance, blocks risky endpoints, and ensures devices are protected with up-to-date security controls.
🔑 Key takeaway: If a device doesn’t meet security standards, it doesn’t get in.
3. Applications: Security Controls
Applications are a primary target for attackers. Zero Trust enforces strong security controls, adaptive access, and microsegmentation to protect apps — whether they’re on-premises or cloud-based.
🔑 Key takeaway: Applications must be safeguarded from exploitation and unauthorized use.
4. Data: Classify, Label, Encrypt
Data is the crown jewel of every organization. Zero Trust focuses on classifying data by sensitivity, labeling it appropriately, and encrypting it at rest and in transit. This ensures that even if attackers break in, the data they steal is unusable.
🔑 Key takeaway: Protecting data goes beyond access control — it requires intelligent classification and encryption.
5. Infrastructure: Assessment and Telemetry
Whether on-premises, in the cloud, or hybrid, infrastructure must be continuously assessed. Zero Trust uses telemetry, vulnerability assessments, and automated policy enforcement to detect threats and reduce the attack surface.
🔑 Key takeaway: Visibility into infrastructure activity is non-negotiable.
6. Networks: Segmentation and Encryption
Networks are no longer flat. Zero Trust enforces network segmentation, real-time threat protection, and end-to-end encryption to limit lateral movement and contain breaches.
🔑 Key takeaway: Assume your network is already compromised — design it to minimize damage.
Bringing It All Together
The Zero Trust Model is not a single product but a mindset shift. By aligning security strategy across these six pillars, organizations build resilience against advanced threats while enabling secure digital transformation.